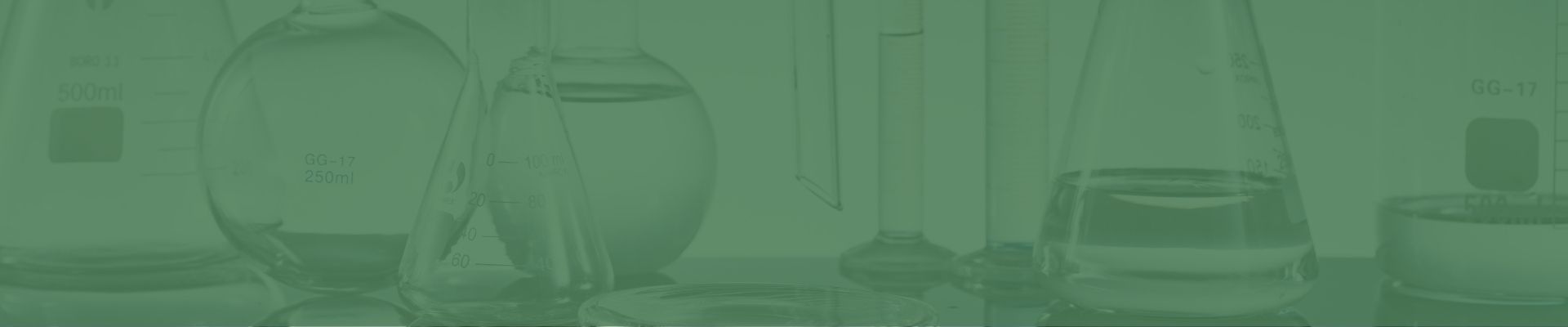
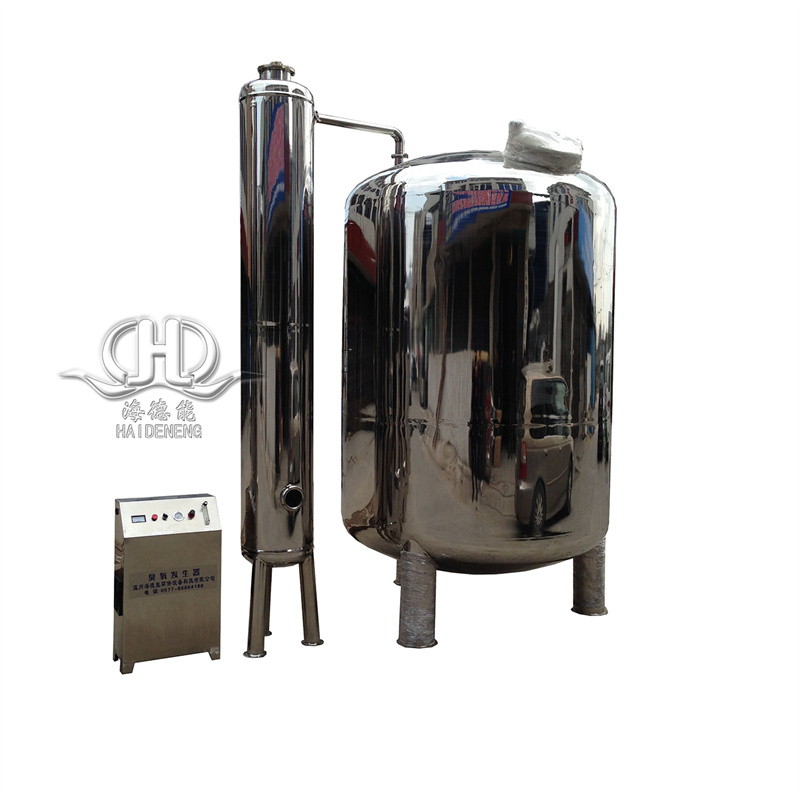
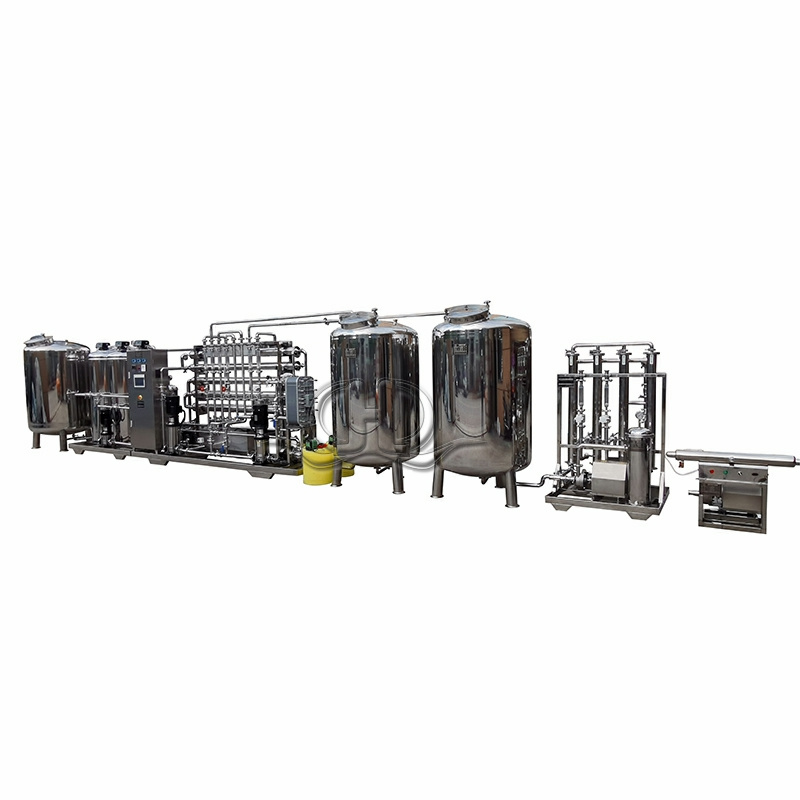
Mineral Water Production Ultrafiltration System
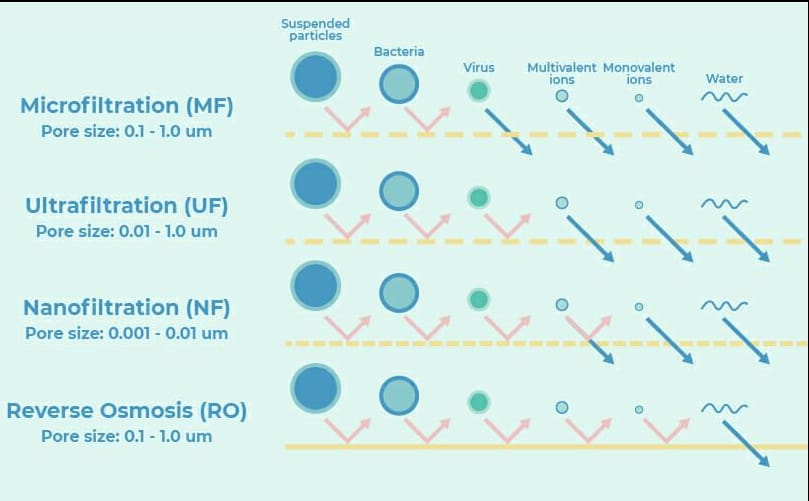
Ultrafiltration is a membrane filtration method that separates substances based on their size and molecular weight. It involves the use of a semipermeable membrane that allows smaller molecules and solvent to pass through while retaining larger molecules and particles.
In various industries, ultrafiltration is utilized for purification and concentration of macromolecular solutions, particularly protein solutions. It is commonly employed in chemical and pharmaceutical manufacturing, food and beverage processing, and wastewater treatment. These applications aim to recycle resources, enhance product quality, and remove impurities.
Additionally, ultrafiltration is crucial in blood dialysis, a medical procedure used to remove waste products and excess fluids from the bloodstream in patients with kidney dysfunction. By selectively filtering out harmful substances while maintaining essential components, ultrafiltration plays a vital role in maintaining the well-being of individuals requiring dialysis treatment.
Overall, ultrafiltration provides an effective means of separation and purification in various fields, improving processes, and contributing to better outcomes in both industrial and medical applications.
Ultrafiltration plays a crucial role in drinking water treatment processes, particularly in the waterworks in Germany. With a capacity of 300 m3/h, ultrafiltration is used to remove particulates and macromolecules from the raw water, ensuring that it meets the necessary standards for drinking water.
Ultrafiltration can be employed as a standalone system in isolated regions experiencing population growth or as a replacement for existing filtration systems in water treatment plants. When dealing with water containing high levels of suspended solids, primary and secondary treatments such as screening, flotation, and filtration are integrated with ultrafiltration as pre-treatment stages.
UF processes offer several advantages over traditional treatment methods. They require no chemicals except for cleaning purposes, ensuring a chemical-free drinking water supply. The product quality remains consistent regardless of the feed water quality, allowing for a reliable source of potable water. Moreover, the compact size of UF plants makes them suitable for various settings.

One of the key strengths of ultrafiltration is its ability to exceed regulatory standards for water quality. With a removal efficiency of 90-100% for pathogens, UF ensures that the treated water is safe for consumption.
However, it's worth noting that UF processes face challenges related to membrane fouling and replacement, which can be costly. To mitigate this issue, additional pre-treatment of the feed water is necessary to avoid excessive damage to the membrane units.
In many cases, ultrafiltration is used as a pre-filtration step in reverse osmosis (RO) plants. By safeguarding the RO membranes from fouling and damage, UF helps to optimize the efficiency and longevity of the overall water treatment process.
Overall, ultrafiltration is an effective and widely utilized method for producing safe drinking water, offering advantages such as no chemical usage, consistently high product quality, and the ability to surpass regulatory standards.
Ultrafiltration (UF) is widely utilized in the dairy industry, particularly in the processing of cheese whey to obtain whey protein concentrate (WPC) and lactose-rich permeate. In a single stage, UF can concentrate whey 10–30 times compared to the initial feed.
Previously, steam heating followed by drum drying or spray drying was the alternative to membrane filtration for whey. However, these methods resulted in products with limited applications due to their granulated texture and insolubility. Moreover, these methods had inconsistent product composition, high capital and operating costs, and often denatured some of the proteins due to the excessive heat used in drying.

In contrast, UF processes for cheese whey offer several advantages over traditional methods:
Improved energy efficiency: UF processes require less energy compared to steam heating and drying methods.
Consistent product quality: Depending on the operating conditions, UF processes can yield whey protein concentrates with protein concentrations ranging from 35% to 80%. This ensures consistent product quality.
Preservation of protein integrity: UF processes operate under moderate conditions, which helps to prevent protein denaturation. As a result, the proteins in the whey concentrate remain intact and retain their functionality.
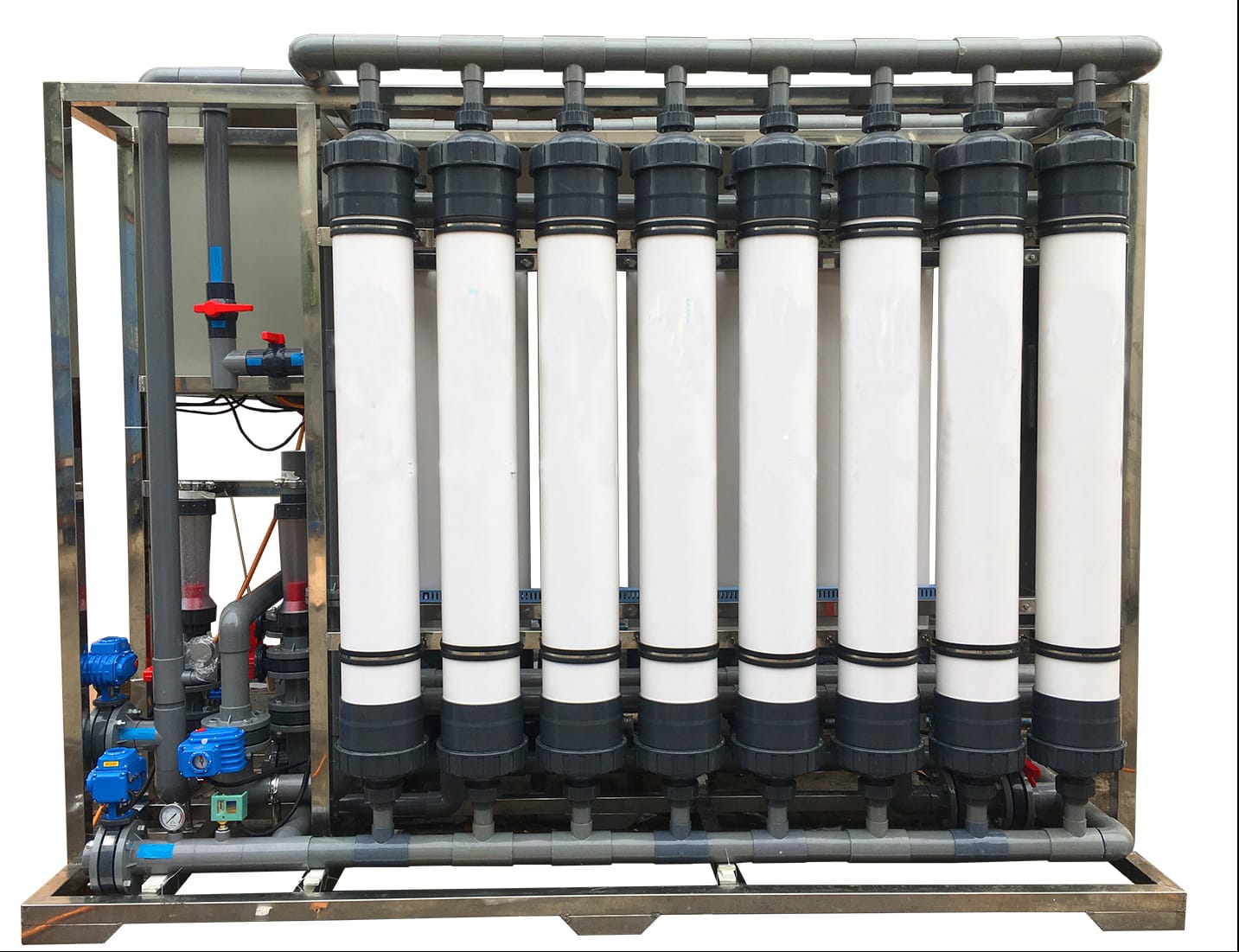

However, UF processes for cheese whey face challenges related to fouling, which can significantly reduce productivity. Cheese whey contains high levels of calcium phosphate, which can potentially lead to scale deposits on the membrane surface. To address this, substantial pretreatment measures are necessary to balance the pH and temperature of the feed, ensuring the solubility of calcium salts.
In summary,UF processes have revolutionized the concentration of proteins in the dairy industry, particularly in the production of whey protein concentrates. They offer energy efficiency, consistent product quality, and the preservation of protein integrity. However, measures must be taken to prevent fouling caused by calcium phosphate deposits.
Ultrafiltration (UF) has numerous other applications beyond the dairy industry. Some additional applications include:
Filtration of effluent from paper pulp mill: UF can effectively remove suspended solids, lignin, and other contaminants from the effluent generated during paper pulp mill operations, helping to meet environmental regulations and produce clean water for reuse or discharge.
Cheese manufacture: UF is used in cheese production to concentrate milk proteins and remove excess water, resulting in a higher protein content in the cheese. This process is often referred to as ultrafiltered milk.
Removal of some bacteria from milk: UF can be employed to remove bacteria, spores, and somatic cells from raw milk, leading to improved milk quality and increased shelf life.
Process and wastewater treatment: UF is utilized in various industries for the separation and removal of solids, colloids, and macromolecules from process and wastewater streams. It is an effective method for reducing suspended solids and organic contaminants, resulting in cleaner water for reuse or discharge.
Enzyme recovery: UF can be employed to separate and recover enzymes from fermentation broths or other sources. The process allows for the purification and concentration of enzymes, enabling their use in various industries, such as food, pharmaceuticals, and biofuels.
Fruit juice concentration and clarification: UF is utilized to concentrate fruit juices by removing water and reducing the volume, resulting in a higher concentration of natural fruit solids and flavors. Additionally, UF can clarify fruit juices by removing suspended solids and cloudiness, resulting in a clearer and more visually appealing product.
Dialysis and other blood treatments: UF is extensively used in dialysis and blood treatment processes to remove waste products, excess fluids, and toxins from the bloodstream. The ability of UF membranes to selectively filter molecules based on size allows for the removal of harmful substances while retaining essential components in the blood.
Desalting and solvent-exchange of proteins (via diafiltration): UF can be utilized for the desalting and solvent-exchange of proteins. This process involves the removal of salts from protein solutions and exchanging the solvent to a desired buffer or solution.
Laboratory-grade manufacturing: UF is commonly used in laboratories for the concentration, purification, and separation of biomolecules, such as proteins, enzymes, and nucleic acids. It is a valuable tool in research and laboratory-scale manufacturing.
Radiocarbon dating of bone collagen: UF plays a crucial role in the extraction and purification of collagen from archaeological bone samples for radiocarbon dating. The process allows for the removal of interfering substances, ensuring more accurate and reliable dating results.








